With the invention of Bitcoin, Satoshi Nakamoto applied another revolutionary concept: technology blockchain. Although it was not given a name by its creator, it started to have so much Spotlight as Bitcoin. After all, blockchain’s first big feat was helping to solve one of the biggest problems to the development of decentralized computing.
Today, blockchain technology is the target of several studies and Software in companies. Everyone seeks to take advantage of the advantages and innovations brought by it. And, in the past 12 years, advances have been made through new networks and different types. Currently, there are three types of most used blockchains on the market:
- Blockchain public;
- Blockchain toilet;
- Blockchain hybrid.
Each network has its own differences, benefits, benefits and scratchs. And it is important to know all of them, since blockchain is usually sold as a silver bullet for various problems. However, it is like all technology, it has its great benefits and also great limitations. In this text we will check how they are and how each one it works.
Public blockchain (not allowed)
THE public blockchain is, for many people, the blockchain by excellence. Bitcoin, which was the first blockchain effectively functional to be launched, is an example of public blockchain. In it no is there any limitation input, the participation on the network is open the whole and any person who wants to participate.
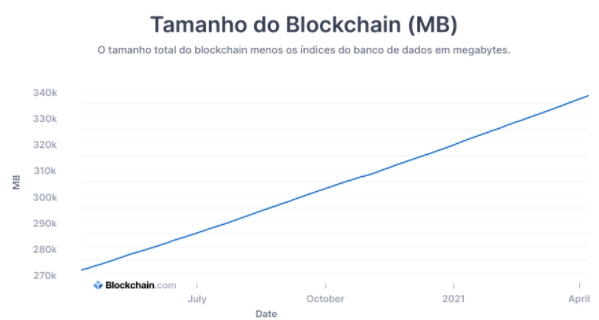
Generally, the few limitations that exist are of a technique. For example, operating a blockchain requires a computer in good condition and very storage space. The Bitcoin blockchain, for example, has almost 400 GB of size. However, once a person meets these requirements, he or she does not need to no authorization, password, or other limitations.
In addition, public blockchains, although they have this name, have a higher degree of privacy. Anyone can check and audit transactions performed on the network in real time. Yet, none personal data or Name of those involved is mentioned in the network, as authors of these transactions no they are identified.
Finally, the people who execute we private blockchains also have anonymity. These nodes are usually scattered around the world, which generates more decentralization and safety to the network. After all, there is not a single individual or company that controls it.
Due to this decentralization, public blockchains dispense with the factor confidence, whether in governments, companies or other authorities. That’s why they’ll always have a cryptocurrency linked to them, which will function as a incentive economical for the network to behave honest. Some examples of public blockchains are:
Private blockchain (permissionada)
The concept of private blockchain was developed by the medium business. Companies started to see the potential blockchain technology, but they saw flaws and / or distrust in the model decentralized. In addition, the transparency and decentralization of public blockchains no is attractive to all sectors
Imagine, for example, the sector Bank officer. The use of a public and 100% auditable blockchain by anyone could leave several exposed data freely. Thus, the company would not be able to protect data sensitive aspects of its operation or obey rules of compliance, among other difficulties.
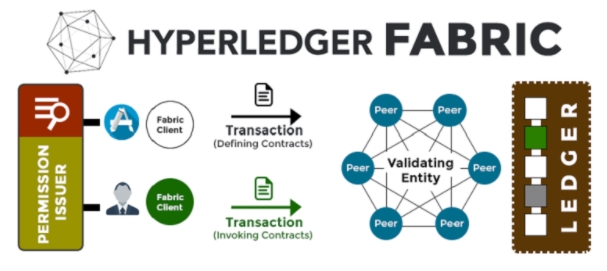
For this reason, companies decided to create their own blockchain networks themselves. These are managed with rules private and have access restricted, usually released by some password or authorization. In addition, as depend gives confidence in a third party (company or government), they usually no have cryptocurrencies tied to them.
Transactions made on a private blockchain are made between your members (P2P). They are linked to Name and identity, being possible to know who did what. However, only people who work in the company that coordinates the network can see and audit the process. Rules of use, responsibilities and possible penalties for use are clearly defined. centralized.
Private blockchains are often used to control Law Suit and products internal or for sales external. A big fridge can use blockchain to track and certify the origin of a beef. A port or company of loads can track back a certain product and check its authenticity from the beginning, and so on.
Like public ones, private blockchains have records unique and immutable. In this way, the falsification or manipulation of the platform data is practically impossible. Companies guarantee that the processes will be well documented and executed, while the customer is guaranteed origin of the product or service received. Some examples of private blockchains are:
Hybrid blockchain
Finally, we have the blockchain hybrid, which, as its name says, is a Mix of the previous types. These networks have characteristics present in both public and private blockchains. As an example, they mix models of privacy partial and even use tokens own, similar to cryptocurrencies.
So, hybrid blockchains can leave some data open and transparent. However, these accesses would be restricted only to those who had permission to operate them. Thus, it would be necessary to authorization access code provided by the company or consortium that management of the tool.
Another issue is that these networks could use tokens, unlike private blockchains. These tokens would be used to fulfill some occupation on the network, such as authenticate documents, transfer values, etc. The entire process of issuing, using and controlling the tokens would be left to the emitters, which differs from decentralized cryptocurrencies. Here are some examples of hybrid blockchains:
Public or private network: which is the best?
This question is inevitable: after all, what is the best type of blockchain that exists? And would hybrid blockchains also be a viable option? The answer is: It depends of how it will be used.
The blockchains public are open to anyone who wishes to use or inspect the network. No one is required to reveal their identity, but they have ample transparency. In addition, your decentralization provides an extra layer of security. Therefore, they are ideal for applications that require anonymity and they cannot to depend third-party confidence.
On the other hand, these networks have a great scale difficulty, i.e, no can withstand a number big of transactions. In this sense, blockchains private have the advantage, because they can have more capacity. However, they lose in the question centralization, which can cause flaws security and attacks.
Regardless of the type of blockchain, the technology has a large potential of growth. The consultancy Gartner estimates that the blockchain could add up to R $ 17 trillion in business value up to 2030. So even if only part of that value is created, the blockchain promises revolutionize – and enrich – Many sectors.
Also read: What is a 51% attack? Can it end Bitcoin?
Also read: What is Ethereum? Beginners Guide
Also read: What is Bitcoin? Complete guide to what you need to know